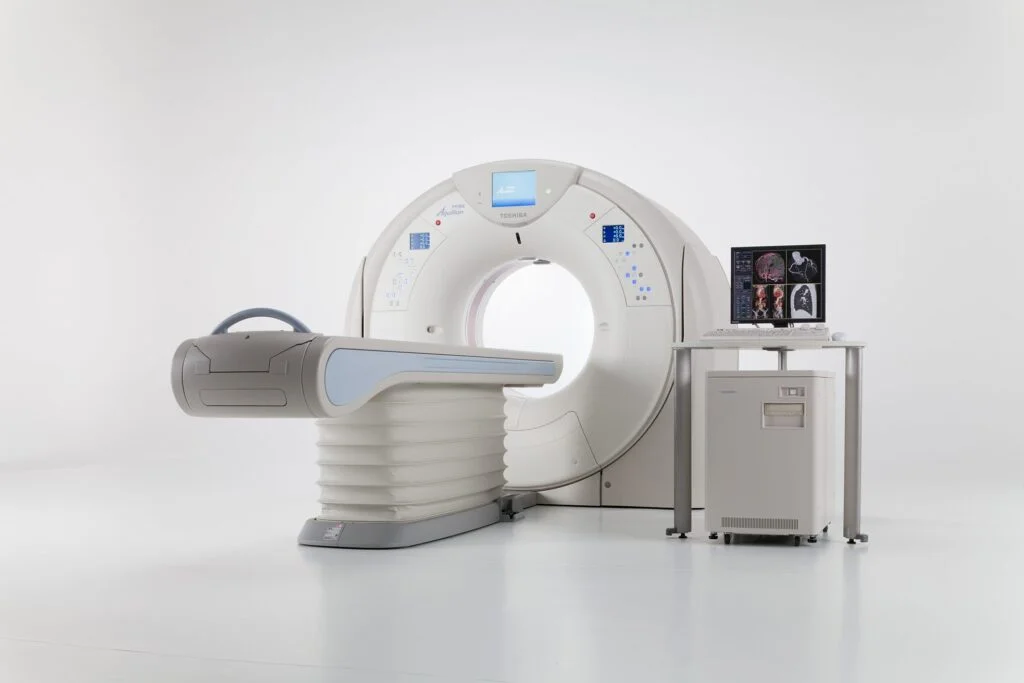
CT Scans are a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to produce detailed, three-dimensional images of internal tissues and structures in the body. They are a key tool in diagnosing and treating tumors. They also have multiple uses in assessing disease severity and monitoring a patient's response to treatment.
A CT Scan consists of a specialized machine that rotates around the body and captures a series of x-ray images from different angles. CT Scans are used in several medical applications, including detecting tumors, assessing injuries and structural abnormalities, planning radiation therapy, and early diagnosis of diseases.
We note that scans should be performed under the supervision of specialized and qualified physicians, as some cases may require preparation before the examination.
 English
English