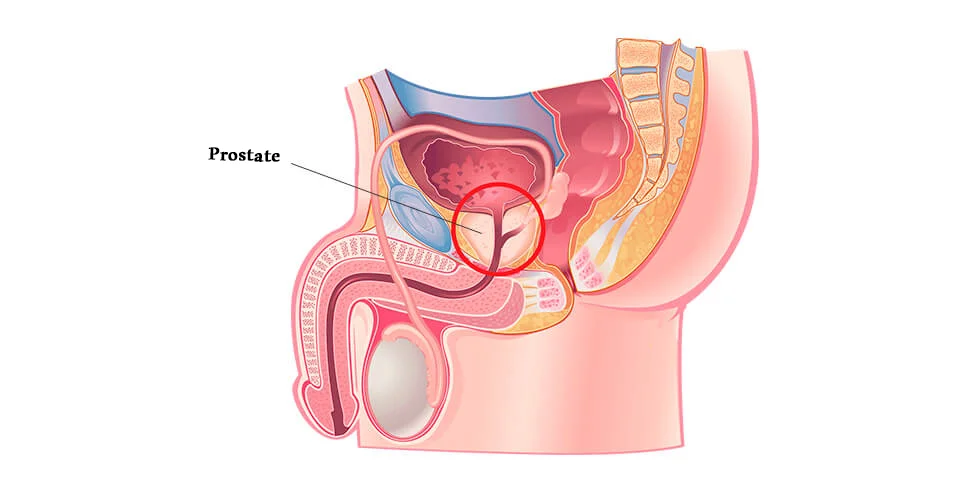
There are some tips and measures that can help prevent prostate cancer, the most important of which include the following:
1- Healthy Nutrition
We recommend eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy proteins such as fish, poultry, and nuts.
2- Physical Activity
You should maintain regular exercise, as it can help reduce the risk of prostate tumors. Therefore, we recommend exercising for at least 30 minutes daily.
3- Avoiding Weight Gain
Obesity and being overweight play a major role in many diseases, including prostate tumors. Therefore, try to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
4- Quit smoking
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of prostate tumors. Therefore, quitting smoking if you are a smoker will be a very important step in preventing prostate tumors.
5- Regular screenings
It is important to have regular screenings. Talk to your doctor about the best screening schedule for you based on your personal risk factors and family history.
 English
English